Cross-site security
DX Core allows you to run multiple sites in a single Magnolia instance. In a multisite scenario, allowing the content of one site to be accessed through the URL of a sibling site hurts search engine optimization (SEO). Web crawlers interpret the sibling content as duplicate content, that is the same content but visible through a different URL. Content should only be accessible through one own domain name for each site.
Magnolia provides two ways to prevent cross-site access:
-
Cross-site security filter grants and denies the permission to access a site through a particular domain name. For example, if you only grant access to the travel site through
travel-demo.magnolia-cms.com, no other URL can be used to access the content. When a user tries to access one site’s content through another site’s domain name, the system displays an HTTP 404 error (page not found). -
Site-specific ACL grants or denies the permission to access a site to a particular role. For example, if you deny the
anonymousrole access to a site then anonymous users will see a login box. They must authenticate themselves in order to gain access to the content through a more permissive role. Use site-specific ACLs if you want to make sibling site content available through the same URL but only for authenticated users such as registered members. A Web crawler such as Googlebot, which is equal to an anonymous user, cannot see the content and will not penalize your SEO efforts for duplicate content.
You can use either mechanism alone or both mechanisms together. If you use them together, remember that the cross-site security filter is executed before the URI security filter in the Magnolia filter chain. This means that the cross-site filter must grant permission to access the site first. Only then will roles and ACLs be evaluated.
The cross-site security filter is executed in the Magnolia filter chain before the URI security filter.
Site names and domain names
A site name identifies a site. The site name is the name of the site
definition node. For example, the name of the travel site is travel.
You need the site name when controlling cross-site access with the
filter or with ACLs.
A domain name is mapped to a site in the domains node under the
site definition. For example, the
travel site has the domain travel-demo.magnolia-cms.com mapped to
it. When a user requests the site with this domain name, content is
served from the path defined in the handlePrefix property. You will
need the domain name when controlling cross-site access with the filter.

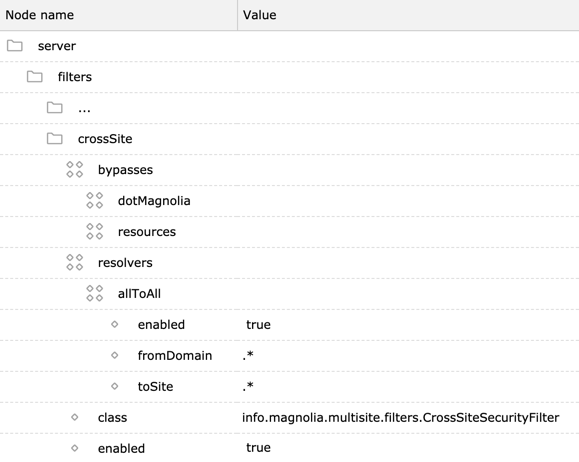
Cross-site security filter
The cross-site security filter is executed in the Magnolia filter chain before the URI security filter. This means that a user must pass the cross-site filter before any ACLs are evaluated. The cross-site filter grants or denies permission to a site when the site is requested through a particular domain name.
The cross-site security filter is configured using resolvers. Each resolver grants access to one site through one domain. If no resolvers exist the filter does not grant access to any site through any domain.
However, a very permissive allToAll resolver is enabled by default. It
grants permission to access all sites through all domains. This is the
starting point from which you can configure more restricted access.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
|
required Resolvers configuration. |
|
required Resolver name. |
|
required Domain name that is used to request a site |
|
required Name of the site that is requested. |
|
optional Protocol used to request the site such as |
|
optional Port number such as |
|
optional Context path is the part of the URL where the Magnolia webapp lives. For
example in |
|
optional Enables and disables the resolver. |
To deny cross-site access, disable the allToAll resolver and configure
new ones.
|
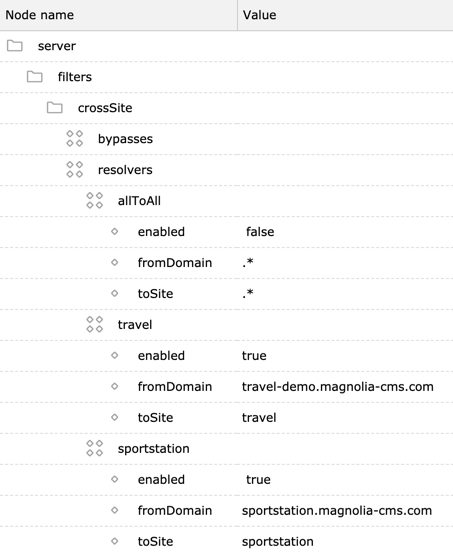
Example
The example resolvers below grant access to the travel site via
https://travel-demo.magnolia-cms.com/
and to the sportstation site via
https://sportstation.magnolia-cms.com/.
This is adequate to prevent cross-site access. If a user requests the
travel site via
https://sportstation.magnolia-cms.com/
they will get a 404 error.
You can test cross-site security by adding these configurations on the
public site and requesting content at
https://sportstation.magnolia-cms.com/travel.html
or
https://travel-demo.magnolia-cms.com/sportstation.
The requests should result in 404 errors.
In specific server configurations, it may also be necessary to add an additional resolver for the administrator/editor to be able to access both the administration and public instances.
Site-specific ACLs
You can also prevent cross-site access using ACLs. This is the recommended practice if you have authenticated users who should have cross-site access when they are logged in.
When whitelisting for multisite, you need to allow both grant and siteGrant rules in SiteUriSecurityFilter.
|
The <site name> parameter makes an ACL rule site specific. You can use the site name in URLs and paths. Enclose the name in angle brackets (< >) at the beginning of the rule. The system applies the ACL when a matching site definition node exists.
The ACL rule here prevents cross-site access from the sportstation site to the travel site.
-
On the public instance, create a new role, for example
cross-site. -
Assign the Web access
Deny:<travel>*rule to thecross-siterole. -
Assign the
cross-siterole to theanonymoussystem user. -
Now, while anonymous requests can fetch content from
https://sportstation.magnolia-cms.com, the standard login form is displayed for requests forhttps://sportstation.magnolia-cms.com/travel.
Filters that control site security
Three filters control site security:
-
Multisite filter (info.magnolia.multisite.filters.MultiSiteFilter) initializes multidomain support and makes domain related properties available in the aggregation state. This filter finds a domain name that matches a name configured in a site definition.
-
Cross-site security filter (info.magnolia.multisite.filters.CrossSiteSecurityFilter) handles cross-site security. It controls site access based on registered resolvers. This filter imports info.magnolia.multisite.CrossSiteAccessResolver, which makes a number of properties available in the filter configuration.
-
Site URI security filter (info.magnolia.multisite.filters.SiteUriSecurityFilter) provides site-aware URI security. This filter extends the Community Edition URI security filter, which checks if the current user has permissions to the requested resource. The following permissions are taken into consideration:
-
URI ACLs of the user’s roles.
-
URI ACLs of the roles in the user group.
-