RMQ Publication module
Edition |
Incubator (services) |
||
Issues |
|||
Git |
|||
Latest |
1.9
|
The RabbitMQ module bundle provides an alternative way of publishing content and synchronizing instances in Magnolia. RabbitMQ is open source message broker software (a.k.a message-oriented middleware) that implements the Advanced Message Queuing Protocol (AMQP).
The Magnolia RabbitMQ modules are suitable for:
-
Environments consisting of more than three public instances.
-
Environments that need to synchronize with other environments.
The RabbitMQ alternative gives you full control over publication and synchronization, while reducing the load on your author environment. Publication is persisted into queues, allowing for easier setup of continuous deployment environments. It’s also possible to audit publication state using the app provided by the monitoring module.
|
This module is at the INCUBATOR level.
Workflow exclusion |
Installing with Maven
Maven is the easiest way to install the module. Add the following to your bundle:
<dependency>
<groupId>info.magnolia.rabbitmq</groupId>
<artifactId>magnolia-rabbitmq-connector</artifactId>
<version>1.9</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>info.magnolia.rabbitmq</groupId>
<artifactId>magnolia-rabbitmq-activation</artifactId>
<version>1.9</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>info.magnolia.rabbitmq</groupId>
<artifactId>magnolia-rabbitmq-monitoring</artifactId>
<version>1.9</version>
</dependency><dependency>
<groupId>info.magnolia.rabbitmq</groupId>
<artifactId>magnolia-rabbitmq-connector</artifactId>
<version>1.8</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>info.magnolia.rabbitmq</groupId>
<artifactId>magnolia-rabbitmq-activation</artifactId>
<version>1.8</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>info.magnolia.rabbitmq</groupId>
<artifactId>magnolia-rabbitmq-monitoring</artifactId>
<version>1.8</version>
</dependency><dependency>
<groupId>info.magnolia.rabbitmq</groupId>
<artifactId>magnolia-rabbitmq-connector</artifactId>
<version>1.7.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>info.magnolia.rabbitmq</groupId>
<artifactId>magnolia-rabbitmq-activation</artifactId>
<version>1.7.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>info.magnolia.rabbitmq</groupId>
<artifactId>magnolia-rabbitmq-monitoring</artifactId>
<version>1.7.1</version>
</dependency>Installing RabbitMQ
Follow the instructions at RabbitMQ to download and install the service. Instructions and packages are provided for all operating systems. It’s also a good idea to enable the management plugin.
| To get started even quicker consider using CloudAMQP to get RabbitMQ as a service. For more detailed instructions see RMQ Setup Example. |
Usage
RabbitMQ can be used for publication and/or synchronization. There exists a single exchange sever with a fanout queue. Exchanges are configured in the connector module.
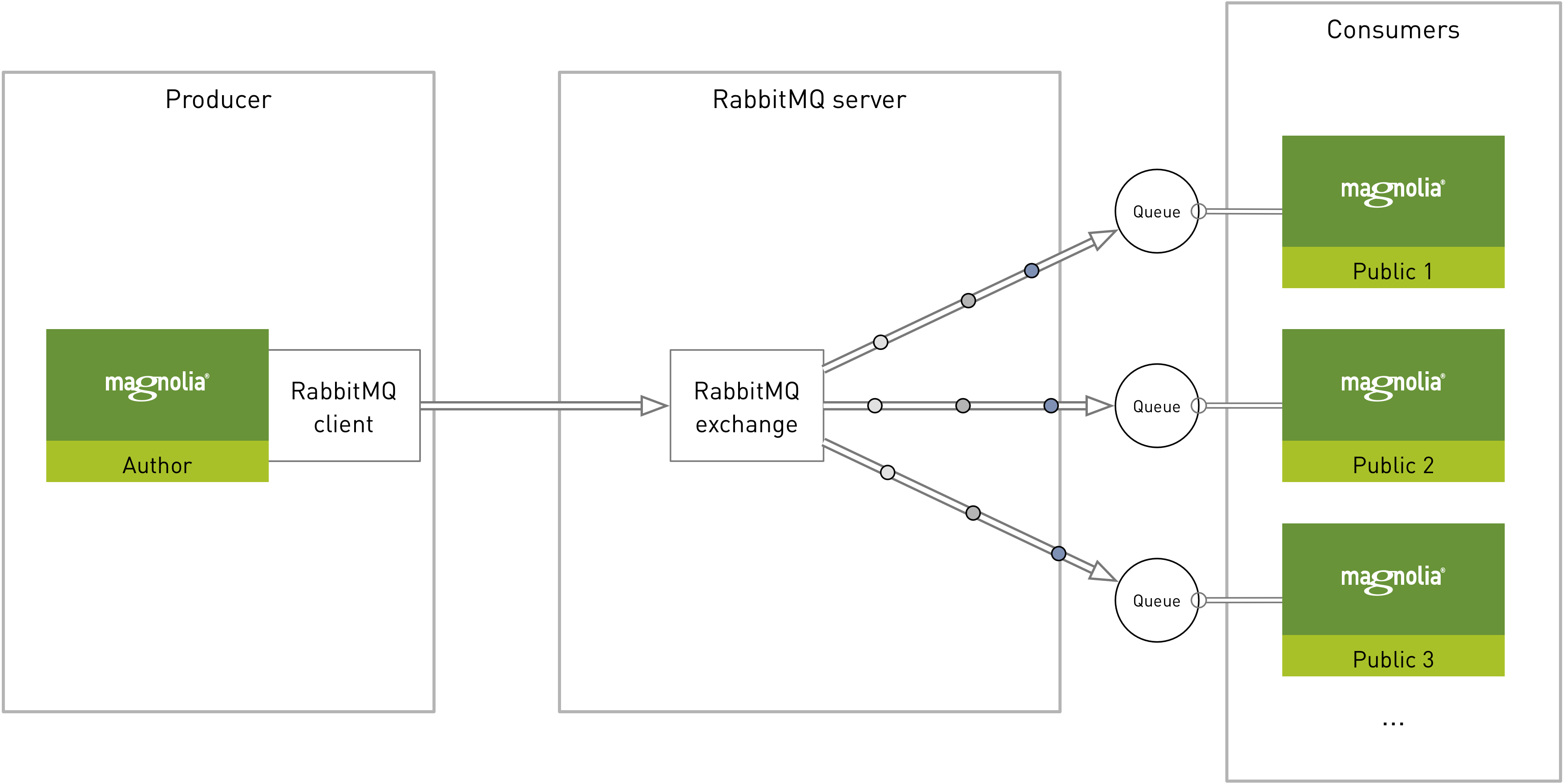
The publication setup would look like this:
Configuration
The exchange is configured on both author (producing instance) and public (consumer instance).
Client
- Example
-
/modules/rabbitmq-connector/rabbitmq-client/sampleClient
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
|
required The value specified here must match the clientName property in the activate and deactivate commands for RabbitMQ. Example: |
|
required Enables and disables the client. Toggling this property restarts the client. |
|
required Address of the broker. |
|
required Password of the user account to connect with. |
|
required Port number to connect the AMQP service. |
|
required Username of the user account to connect with. |
|
required Virtual host to connect to. |
Exchange
The exchange is the kind of router that the queues connect to. The producer instance pushes messages to the exchange and the exchange then decides what to do with them. You must configure the exchange configuration on the author or producing instance.
- Example
-
/modules/rabbitmq-connector/rabbitmq-client/sampleClient/exchangeConfig
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
|
required The name specified here must match the exchangeName property in the activate and deactivate commands for RabbitMQ.
|
|
required Exchange type. See AMQP 0-9-1 Model Explained for more information. Options:
|
Queue
A list of queue definitions to bind with the exchange should be configured under the node queueConfigList.
- Example
-
/modules/rabbitmq-connector/rabbitmq-client/sampleClient/exchangeConfig/queueConfigList/queue
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
|
optional Automatically deletes the queue when last consumer unsubscribes. |
|
optional, default is Used for only one connection. Queue is deleted when that connection closes. |
|
required Name of the queue. |
|
optional Key used to route messages. The queue binds to the exchange with the routing key. Applicable when |
Consumer
Consuming messages on a public instance is called activation or publication.
- Example
-
/modules/rabbitmq-connector/rabbitmq-client/sampleClient/consumerDefinition/activationConsumer
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
|
optional Used for monitoring. An ACK exchange is bound to a queue on which activation confirmation messages are sent. |
|
optional, default is Automatic acknowledgement. |
|
required Name of the client to use. |
|
required Consumer class which implements info.magnolia.rabbitmq.activation.jobs.AbstractMQConsumerJob.
|
|
required Enables and disables the consumer. |
|
required Name of the consumer. |
|
optional, default is Notify the user of the status. |
|
optional, default is Set the consumer for test mode. |
|
optional, default is Options are |
|
optional, default is Authorizes the signature and data of message from other instance. |
Commands
The RabbitMQ Activation module installs the activation commands here: /modules/rabbitmq-activation/commands.
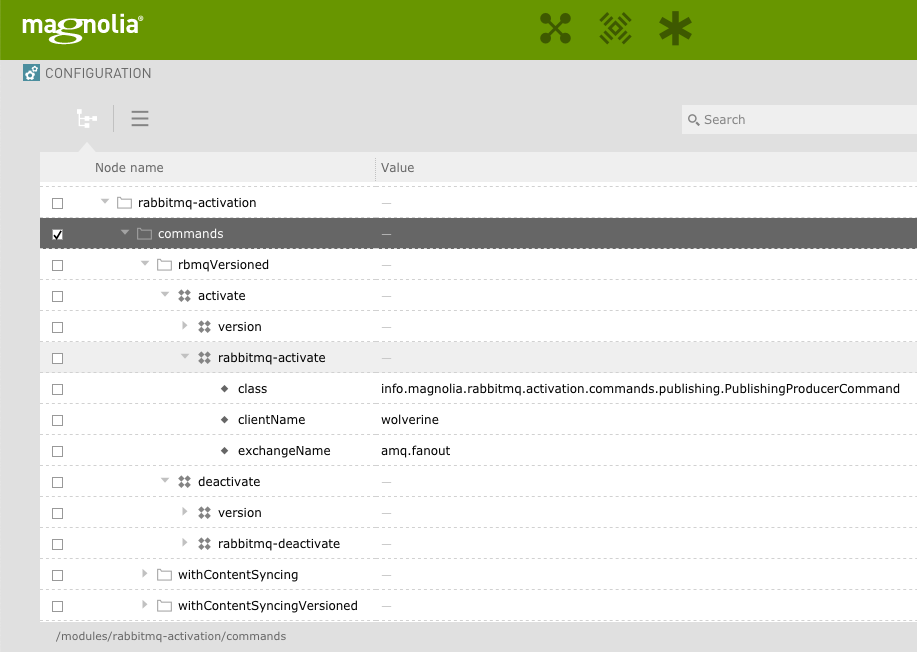
Catalogs
You can select commands/catalogs to match your purpose for using RabbitMQ.
Here are a list of the catalogs with a description of their purpose. Inside each catalog folder you will find a "command chain" node which chains together the commands that should be performed.
| Catalog | Command chain | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Allows you to hook into transmission over RabbitMQ once you have done a standard activation. Calls the standard activation command first and then calls |
|
|
Same as |
|
|
Replaces standard activation with RabbitMQ versioned activation. Calls the versioning command first and then calls |
Command configuration
The commands themselves rabbitmq-activate and rabbitmq-deactivate have the following configuration options.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
|
required Configured client name. The |
|
required Configured exchange name. The |
|
optional , default is When set to true message acknowledgements are delegated to RabbitMQ. Set to |
|
optional , default is Stack size allows you to send more nodes per activation message, making messages bigger but reducing the number of messages in the queue. |
|
optional , default is Blocktime in seconds. Works only if |
|
optional Works only if |
|
optional Minimum number of public instances to wait ack for. Works only if |
Activation mechanism
Each activation is prefixed with a BOA (Beginning Of Activation) message and post-fixed with a EOA (End Of Activation) message. When the consumer receives a message on a public instance, the message is stamped with the identity of the receiver and send back to the ACK queue. When the author receives the message, the author knows exactly if the message started consuming the activation. In addition, identifying the activation in queue with BOA and EOA allow identification of TX inside the the queue.

Monitoring
RabbitMQ monitoring allows for public instances to confirm publication with the author instance. In this setup author and public both play the producer/consumer role. This is an optional configuration, known as acknowledgment, for those wishing to audit publication status.
For an acknowledgement setup:
-
A simple fan out pattern is used for activation from one Magnolia author instance to N public instances.
-
Acknowledgements are not delegated to RabbitMQ. Instead, notifications of activation success or failure are sent back to the acknowledgement (ACK) exchange for consumption by author.
-
The AMQP
0-9-1(Advanced Message Queuing Protocol) messaging protocol is used.
The publication w/ acknowledgement setup would look like this:
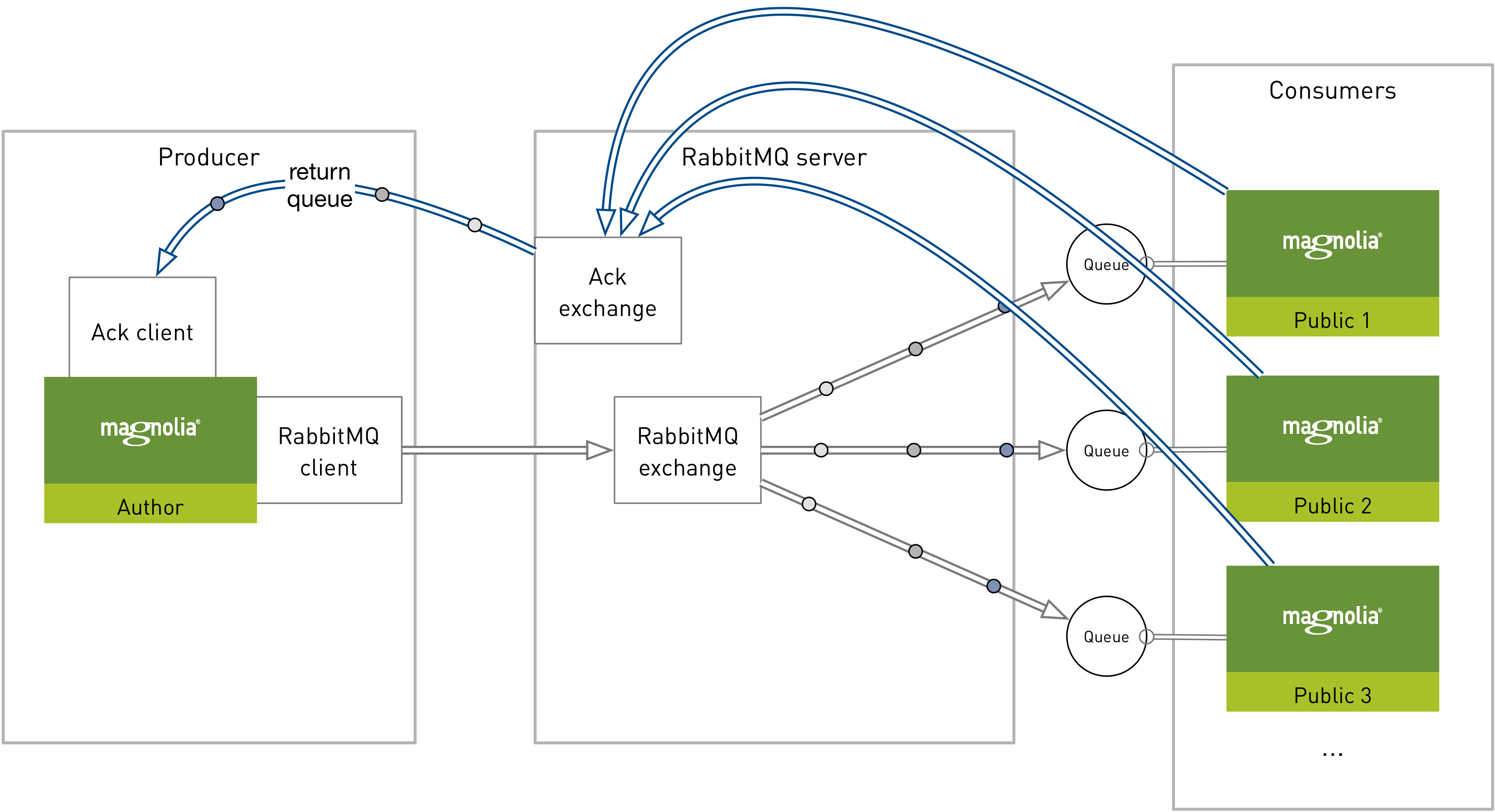
Public monitoring app
The Public Monitoring app displays the states of any instance that is consuming on a queue. The app will show information messages containing the status of activation grouped by the user who created the request.
Activation states:
-
IOA Message in queue not yet received by consumer but sent by author.
-
BOA Beginning of activation, message received by consumer, nodes will be consumed shortly after.
-
EOA End of activation, message consumed and remitted after all nodes were successfully consumed.
-
EXA Exceptions on activation, nodes were not processed correctly and the consumer sent the exceptions to the author before shutting itself down.
| If an activation fails, the message is put back into the queue and an exception is pushed into the acknowledgment queue. The consumer is then stopped allowing you to fix the problem and to remove the faulty instance from the load balancer. |
REST endpoints
REST endpoints are used for controlling and monitoring publication.
| By default the endpoints are not enabled. They must be explicitly configured through the Security app to be available to the outside world. |
The monitoring module provides three endpoints.
Synchronization State
The SyncState REST service gets the current state of publication immediately (without checking the ACK return queue).
This service stores values in properties on the node /modules/rabbitmq-activation/syncNode`. These properties should not be changed by hand. They are not configuration settings.
|
To enable the SyncState service for anonymous access add the following permissions to the rest-anonymous role:
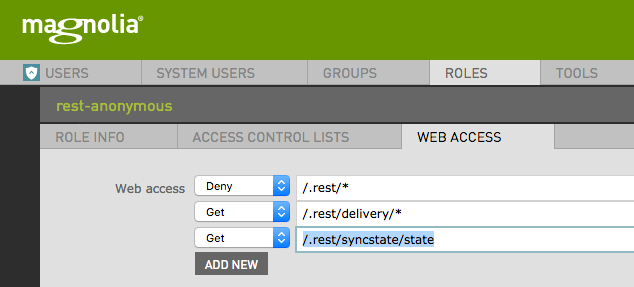
You can call the REST endpoint using cURL:
curl http://<hostname>:<port>/<context>/.rest/syncstate/state{"seqNbr":2011,"stamp":1467280192928,"topoTag":""}Public monitoring
The public monitoring REST service gets the results of all consuming instances returning messages on the ACK queue. This service is used by the Public Monitoring app.
You can access the monitoring screen at http://<hostname>:<port>/<context>/.resources/magnolia-rabbitmq-monitoring/webresources/visualisations/public_monitoring.html or in the Public Monitoring app.
|
To enable the public monitoring service for anonymous access add the following permissions to the rest-anonymous role:
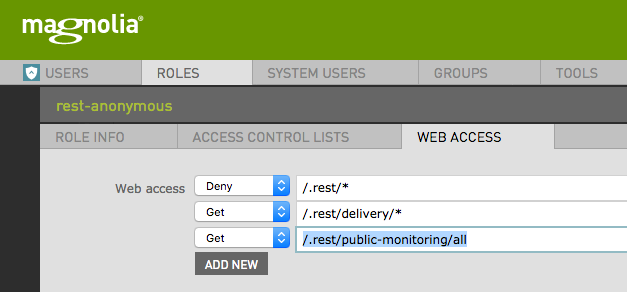
You can call the REST endpoint using cURL:
curl http://<hostname>:<port>/<context>/.rest/public-monitoring/all[{"workspace":"dam","address":"192.168.10.85","name":"administrators-MacBook-Pro.local","syncStamp":"1466422838236","diff":"0","uuid":"2acd7055-7168-4926-b66a-47400ab78d2e","seqNbr":"1977","exceptions":"{}"}]| Property | Description |
|---|---|
|
Workspace of last activated node. |
|
IP of consuming instance. |
|
|
|
Timestamp of last activated node. |
|
Difference on seqNbr with other instances who activated a similar node. |
|
UUID of last activated node. |
|
Sequence number of last activated node. |
|
Exceptions that may have occurred. |
Client control
The client control REST service allows you to restart the consumer on the remote instance.
To enable the client control service for anonymous access add the following permissions to the rest-anonymous role:
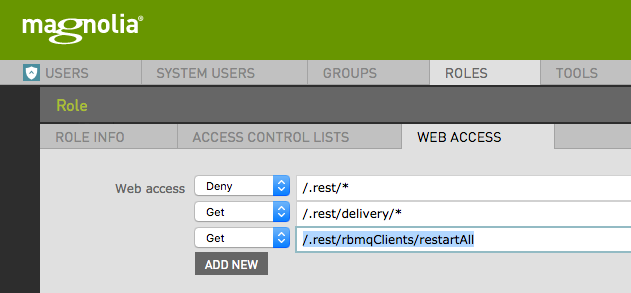
You can call the REST endpoint using cURL:
curl http://<hostname>:<port>/<context>/.rest/rbmqClients/restartAll